Embedded C Programming And The Atmel Avr Pdf Free Download

Number of employees 5,000 Website Atmel Corporation is an American-based designer and manufacturer of, founded in 1984. The company focuses on embedded systems built around. Its products include microcontrollers (, AVR, 32-bit -based, automotive grade, and 8-bit derivatives) radio frequency (RF) devices including,, and devices, symmetric and asymmetric security chips, touch sensors and controllers, and application-specific products. Atmel supplies its devices as standard products, (ASICs), or application-specific standard product (ASSPs) depending on the requirements of its customers. Atmel serves applications including,,,,,, and. It specializes in microcontroller and touch systems, especially for.
Atmel's corporate headquarters is in, in the. Other locations include;;;;;;;;;;;. Atmel makes much of its product line at vendor fabrication facilities. It owns a facility in that manufactures its XSense line of flexible touch sensors. In 2016, agreed to buy Atmel for US$3.6 billion in a deal brokered by and. Logo from 1984 to 2012 Founding and 1980s growth [ ] Atmel Corporation was founded in 1984, by George Perlegos. Atmel was an acronym for “advanced technology for memory and logic”.
Microchip Technology Inc. Is a leading provider of microcontroller, mixed-signal, analog and Flash-IP solutions, providing low-risk product development, lower total. Books and resources to get started using Atmel devices recommended by the Atmel University Program.
Perlegos had worked in the memory group of in the 1970s and had co-founded to manufacture memory. Using only US$30,000 in capital, Atmel was initially operated as a fabless company, using and to make the chip wafers. The first Atmel memory products used less power than competitors. Customers included,, and. In 1987 Intel sued Atmel for patent infringement.
Rather than fight the patent claim, Atmel redesigned its products to use different intellectual property. Download Workplace Management Ohno Pdf Converter. These had better performance and even lower power consumption. In addition, Atmel then entered the business that Intel had focused on. Atmel used US$60 million in venture capital for the 1989 purchase of a fabrication facility from in Colorado Springs.
Atmel then invested another US$30 million in manufacturing technology. 1990s expansion [ ]. Back side In 1991, Atmel expanded the Colorado facility after acquiring Concurrent Logic, a (FPGA) manufacturer. The company made its (IPO) in 1991 which yielded more than US$65 million.
1994 saw Atmel enter the microprocessor market. The first Atmel flash memory microcontroller was based on the.
The controller executed an instruction for every clock cycle, as opposed to the 12 cycles that legacy 8051 parts required. In 1994, Atmel purchased the EEROM assets of Seeq Technology ( acquired the rest of Seeq in 1999). In 1995 Atmel was among the first companies to license the, creating initially its AT91 family of devices, followed by the SAM family, and more recently a full selection of Cortex-based solutions, including ones based on the ultra-low-power.
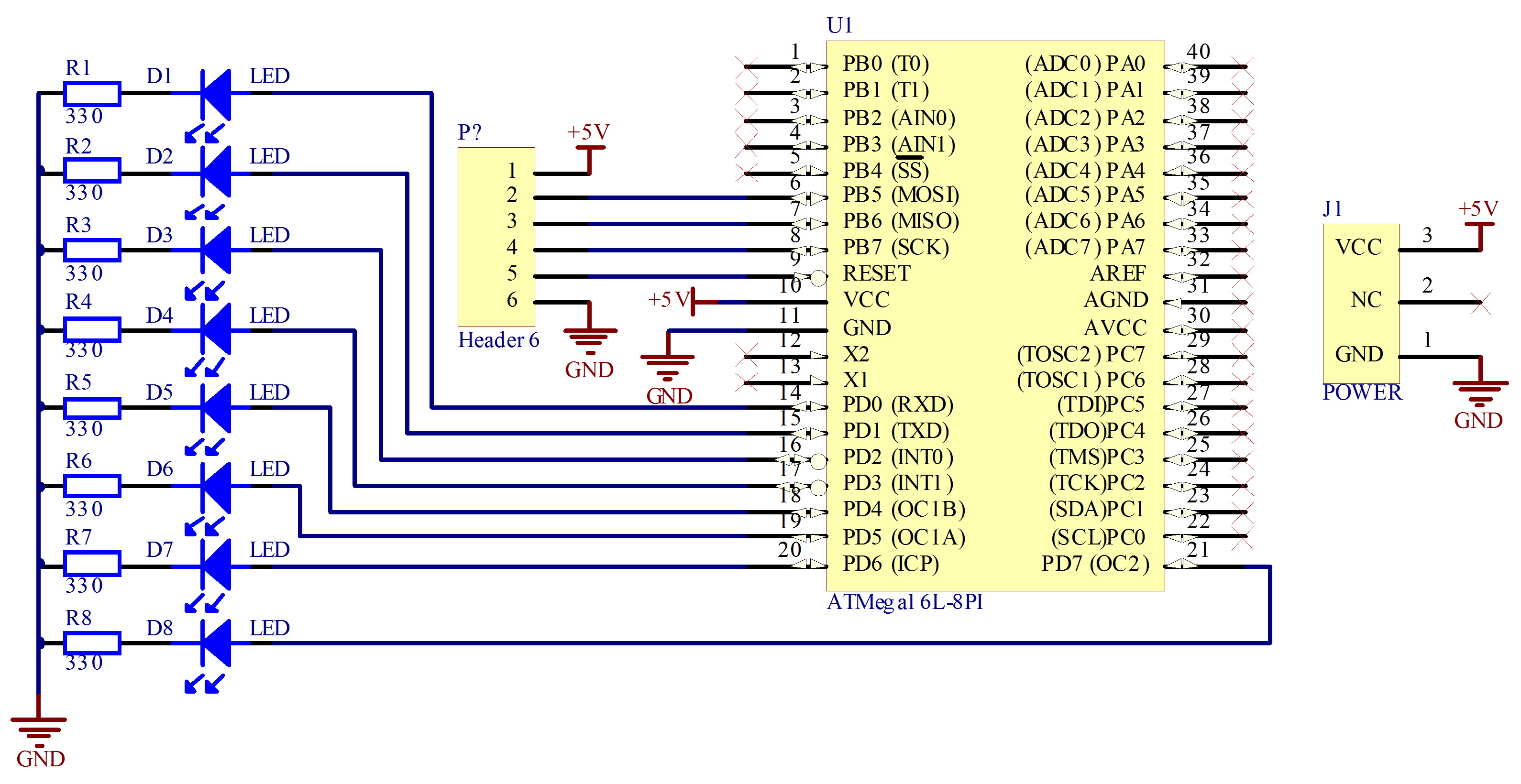
Atmel now has dozens of families of ARM-based devices. In 1995, Atmel opened a fabrication facility in, France. Atmel acquired European Silicon Structures and Digital Research in Electronic Acoustics and Music (DREAM) in 1996. Atmel formed a design team in to develop the line of microcontrollers. This team combined technology of former students at the with Atmel's expertise in flash memory. These 8-bit chips were first developed in 1996. The AVR chip is the basis of most development boards.
In 1998, Atmel purchased part of TEMIC from, which provided them with a fab in Germany as well as part of MHS from Vishay that gave them a fab in,. In September 2000, Atmel acquired a fabrication plant in,, from, via a £28 million grant from the UK government and paying Siemens around US$35 million.
Streamlining [ ] Atmel streamlined operations with a strategy called 'fab-lite'. This started in 2005 when Atmel sold the MHS fab in Nantes France to Xbybus. In February 2006, Steven Laub became a director and in August president and chief executive officer. Under Laub Atmel divested more manufacturing plants and business lines. Atmel announced the sale of its North Tyneside facility (Fab9) on October 8, 2007.
The manufacturing equipment was sold to Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. () and the property and associated land to Highbridge Business Park Limited. In 2008 Atmel sold their fab in Germany to Tejas semiconductor. In 2010 Atmel received approval from the French government to sell its fab to Germany-based LFoundry GmbH, while retaining their design center there. Atmel completed the sale of their Secure Microcontroller Solutions smart card business to INSIDE Secure. In February 2011, Atmel sold its Digital Research in Electronics, Acoustics and Music (DREAM) business, which sold products for karaoke and other entertainment machines, for US$2.3 million.
Atmel's serial interface flash memory products were sold to Adesto Technologies in October 2012. Acquisitions [ ]. Atmel corporate headquarters in San Jose California As Atmel divested several fabs and ancillary business lines, Laub also oversaw acquisitions.
One strategy was to participate in the touch screen market, both in the semiconductor chips and the sensors themselves. In 2008 Atmel purchased Quantum Research Group Ltd. (now known as Atmel Technologies Ireland Limited, a wholly owned subsidiary), a supplier of capacitive sensing technology.
Work done at Quantum, led to the 2012 release of Atmel's XSense product line, a flexible touch screen based on copper mesh electrodes. Atmel moved into technology.
They completed the acquisition of Advanced Digital Design S.A, a Spanish company that develops. Ozmo Devices, which developed products for, was acquired by Atmel in December 2012. Ozmo was founded in 2004 as H-Stream Wireless by Kateljin Vleugels and Roel Peeters, and was based in. In 2012, Atmel had approximately US$1.4 billion in annual revenue, with over 60% of their revenue from microcontrollers, and net income of US$30 million. Atmel purchased the product lines of in March 2013. Atmel purchased Newport Media in July 2014. This will provide Atmel further capability in wireless Bluetooth and Wi-Fi.
Acquisition by Microchip Technology [ ] In 2016, agreed to buy Atmel for $3.6 billion. And served as financial advisers to Microchip and Atmel, respectively. The company had previously heard offers from and in 2015, and the deal with Microchip is expected to be finalized at the end of Q2 2016. Previously in October 2008, Atmel received an unsolicited offer from and, estimated at US$2.3 billion. The offer was eventually rejected and the companies gave up on their attempt.
Atmel merged with on July 2016 after prolonged negotiations for US$3.56 billion. Products [ ] Microcontrollers [ ]. Atmel ATMEGA32 microcontroller A large part of Atmel's revenue is from microcontrollers.
These include the 8- and 32-bit microcontrollers, microprocessors, and ARM-based flash microcontrollers. In addition Atmel still makes microcontrollers that use the architecture, albeit improved to do single-cycle instructions. Supporting the microcontrollers is the Atmel Studio 7 which Atmel offers for free. They also provide an Atmel Software Framework. Wireless / RF [ ] To provide for the (IoT), Atmel offers dual-band 2.4 GHz/5 GHz a/b/g Wi-Fi chips from its Ozmo acquisition.
Also, Atmel offers 2.4 GHz b/g/n Wi-Fi chips WILC1000/WILC3000 and WINC1500 from its Newport Media, Inc acquisition. WINC1500 provide a full 802.11 b/g/n network controller with full ip stack TCP/IP, UDP with upper layer protocols as DHCP, DNS, HTTP, SNTP, TLS etc.
Also, Atmel makes wireless transceivers using regional 700/800/900 MHz, as well as global 2.4 GHz frequency bands, Some chips are standalone transceivers while others are integrated with a microcontroller. They also sell the Zigbit module that comes with FCC certifications. Atmel also makes remote control RF products using the license-free (industrial scientific medical) frequencies (5.8 GHz, 2.4 GHz, 868 to 928 MHz, 433 MHz, and 315 MHz). The wireless segment also provides chips for tracking, access and identification.
Finally, Atmel offers a line of IR controllers that can support infrared as well as RF wireless. [ ] Touchscreen [ ]. Atmel XSense is a flexible touchscreen film that uses a copper mesh instead of indium tin oxide (ITO). Atmel makes both touchscreen controller ICs and its XSense flexible touchscreen.
The company makes sensor hubs that manage accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers. These sensors give consumer products and embedded systems. The sensor hub offloads the main application processor and allows product functionality without the need to power the main processor. Atmel also makes simple touch controller chips for buttons, sliders, and wheels used on industrial and consumer products. The touch wheel interface became popularized by the Apple. To support the application of its touch controller chips, Atmel provides a free QTouch library of software routines. [ ] Memory [ ] Atmel's original business was in memory, and it still sells several memory products.
It offers serial and parallel EEPROM, as well as one-time programmable (OTP) EPROM. In addition, it offers secure memory with its CryptoMemory product line of EEPROMS in capacities from 1 to 256 kbits. [ ] Security [ ] In addition to the secure memory mentioned above, they have the CryptoAuthentication product lines that provide hardware authentication capability with both symmetric and authentication. These ICs are used in many applications, including secure access, communications, control, and to prevent cloned products like batteries or ink cartridges not approved by the product manufacturer. Atmel's CryptoRF products add hardware encrypted security to RFID applications. Finally Atmel offers a trusted platform module that gives strong hardware-based public key () security for both personal computers and embedded processors on a single chip.
[ ] Analog [ ] Atmel makes driver chips. It also has a line of digital-output temperature sensors.
The company also makes power management and analog companions (PMAAC) that combine a group of discrete ICs often used in handheld or battery-powered products. Integrated functions include audio (compressor-decompressor), battery chargers, and stereo. [ ] Custom [ ] These products include custom integrated circuits designed to meet specialized single-customer requirements. Products include, products with military and aerospace applications, and application-specific standard products (ASSP) for space applications, power management, and secure cryptographic memory products. [ ] Automotive [ ] Atmel modified or specialized many of its products for the automotive market. These products often have a wider temperature range or are specially qualified for automotive applications.
These products include car access, touch control, radio, CAN, VAN, and LIN Bus networking, battery management, high-temperature drivers, and serial EEPROMs. [ ] Smart energy [ ] Atmel also has chips specialized for the smart energy and smart metering markets. These chips combine microprocessors with tamper-proof hardware security and power line communication modems. The parts also integrate for accurate metrology.
[ ] See also [ ]. US Securities and Exchange Commission. February 26, 2013. Retrieved September 27, 2013.
United States Securities and Exchange Commission. February 28, 2014. • ^ Picker, Leslie (2016-01-19)..
The New York Times.. Retrieved 2016-01-21. • ^ Assis, Claudia.. Retrieved 2016-01-21.
The Silicon Valley Historical Association. Retrieved September 27, 2013. •, 'Atmel Corporation History' • ^, 'Atmel Corporation' •, 'Atmel’s Self-Programming Flash Microcontrollers', Whitepaper. •, '8051 Single Cycle Core Microcontrollers', Flyer. Retrieved October 3, 2013. The CPU Shack museum.
February 5, 2011. Retrieved September 27, 2013. • Andrew Thomas (September 18, 2000).. The Register.
Retrieved September 27, 2013. • EBN (Electronic Buyer News). • Mark LaPedus (March 1, 2010).. Retrieved September 27, 2013. • Peter Clarke (October 1, 2012).. Retrieved September 27, 2013.
• ^ engadget. • Peter Clarke (December 21, 2012).. Retrieved September 27, 2013. • Anne Francoise Pele (March 8, 2013)..
Retrieved September 27, 2013. Windows Toolkit 2.5 Beta 1 Download. Atmel press release.
July 7, 2014. Retrieved July 24, 2014. • • Beckerman, Josh.. Wall Street Journal.. Retrieved 2016-01-21. • Research, Zacks Investment.. Zacks Investment Research.
Retrieved 2016-01-21. • Margaret Kane (October 2, 2008).. Retrieved September 27, 2013. • Steven Laub (October 2, 2008).
Archived from (PDF) on October 10, 2008. Retrieved September 27, 2013.
• Benjamin Pimentel (October 29, 2008).. Market Watch. Retrieved September 27, 2013. EE Times India. April 17, 2009.
• • • Haakon Skar (Atmel) (November 1, 2011).. Electronic Products. Retrieved October 3, 2013. External links [ ] Wikimedia Commons has media related to.
I'm not sure if you know, but there’s these things called 'bookshops', some are even 'online' (this means you can access them online). What these places do is 'sell' the book so that you can 'buy' the book (I can explain these concepts if you're not sure).
This enables the 'Author' and everyone else to generate income from the sale to make a living (this is a concept whereby you can afford to live in modern society through the work that you do). Of course if you don’t want to pay, that’s fine as there are thousands of tutorials, Free eBooks and even forums like this where you can ask a question on a specific topic. If you don't think the book is worth it's price, why would you like to have it???
If you don't have much money, there are cheaper ways. For almost the same price you'll get a very good book, an AVR butterfly and some more hardware: If this is still too expensive look here: There is no need to steal.
You can get so much for free. All the help in this forum is for free. It's a good feeling to learn and work with peace of conscience. And you have more advantages than disadvantages. Check it out! Regards Sebastian. Vaidyasp1 wrote: Do anyone have this ebook.
If yes can you please upload!! Embedded C Programming and the Atmel Avr - by Richard H.
Barnett, Larry O'Cull, 520 pages I am seeing this everywhere - even at work! I buy a lot of books. At work, I have loaned out a few books, only to never have them returned.
I've stopped loaning them out. I figure that, if my personal growth is important enough for me to spend $80.00, $100.00, or more for a book, it should be that important to you. Why should I pay for a real or e-book and loan or give it to another who is too cheap to invest in him/her self.
I spent $80.00 on a book on CNC programming this past week. Now, the whole fabrication department wants a copy of the CD that came with it. If your viewpoint about learning is such that you need to get everything free then, your learning isn't worth a damn.
If you have to steal other individuals work and livelyhood, that tells me exactly what kind of individual you really are. And, if you have to steal, this is a reflection of character you have - one we don't want in the embedded microcontroller industry!
If you want the O'Cull AVR book - PAY FOR IT.